Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of Production Stages in Playing Card Making Machines
Introduction to the End-to-End Production Process
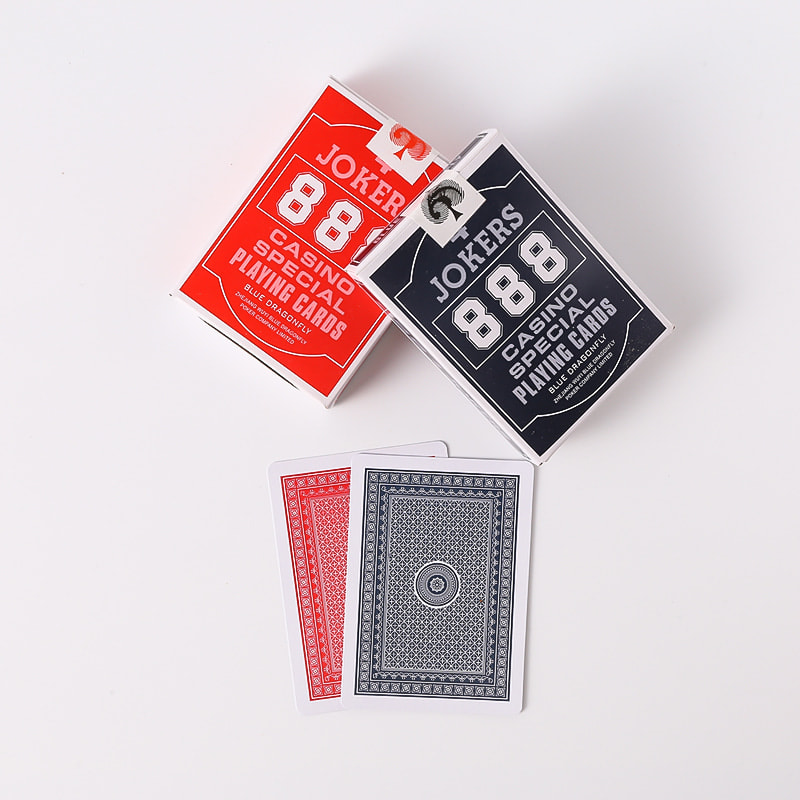
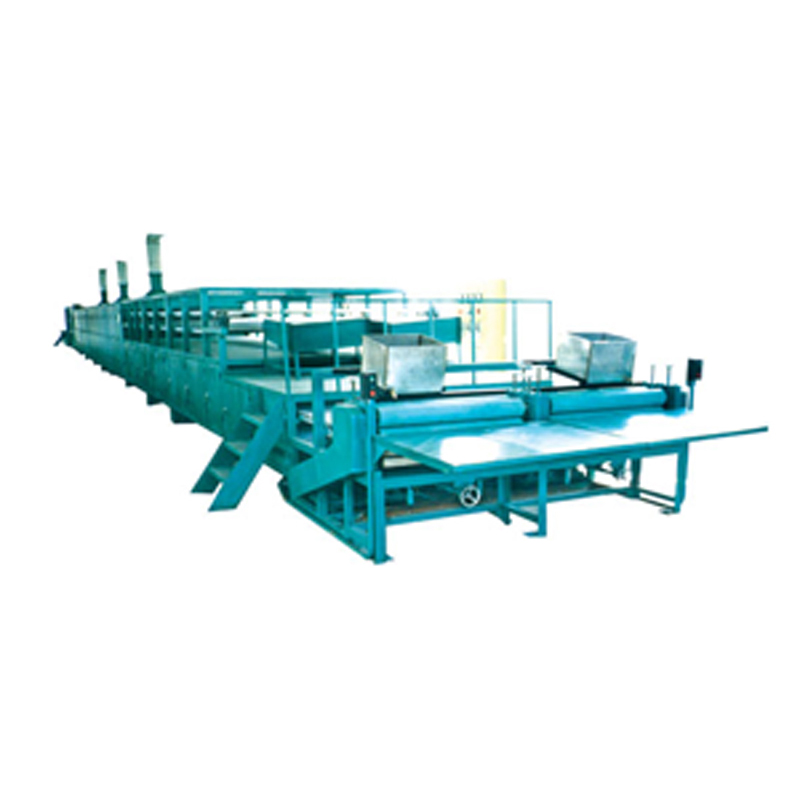
The manufacturing of playing cards is a highly detailed process that requires precision, consistency, and speed. A well-designed Playing Cards Making Machine integrates several key production stages into a streamlined workflow. From raw paper handling to final card packaging, each phase plays a vital role in delivering high-quality, uniform decks suitable for both casual and professional use. Understanding these major steps helps illustrate how modern card production balances efficiency with craftsmanship.

Stage 1: Paper Feeding and Alignment
The process begins with the feeding of raw paper or pre-coated cardstock into the system. High-precision sheet feeders or continuous roll feeders ensure the material enters the machine in good alignment. This step is crucial, as any misfeed can result in misregistration in the print stage or errors in the cutting phase. The feeder may also include mechanisms for paper flattening and static removal to ensure smooth transportation through the system.
Stage 2: High-Precision Printing
Once the paper is correctly positioned, it moves to the printing section. Depending on the configuration, the machine may use offset, flexographic, or digital printing technology to apply the designs. Most playing cards require double-sided printing—faces on one side and a uniform back design on the other—so alignment and color accuracy are critical. Advanced systems often include real-time registration control and color calibration for consistent quality throughout the batch.
Stage 3: Drying and Curing (If Required)
If UV inks or coatings are used during printing, a drying or curing stage follows. This section may feature UV lamps or thermal units that rapidly set the ink to prevent smudging, bleeding, or transfer during handling. Quick and effective drying ensures that the paper moves into subsequent stages without delay or contamination, maintaining production speed and cleanliness.
Stage 4: Laminating or Coating for Durability
To enhance the durability and tactile feel of the cards, a lamination or surface coating process is typically applied next. This can involve either thermal lamination or aqueous coating, depending on the required finish—glossy, matte, or textured. Laminating protects the print from wear, moisture, and fading, while also giving the cards a smooth, professional surface ideal for shuffling and dealing.
Stage 5: Precision Cutting and Corner Rounding
After the lamination or coating phase, the printed sheets are fed into a cutting section. Guillotine cutters, rotary die-cutting systems, or high-speed punching tools are used to slice the sheets into individual cards. Since precision is key to uniformity, these machines are calibrated to cut within tight tolerances. Most systems also include automatic corner-rounding to give cards their signature smooth edges, which improves handling and extends lifespan.
Stage 6: Collating and Deck Assembly
Once individual cards are cut, they are automatically sorted and arranged into complete decks. Advanced machines use collation mechanisms that verify the sequence and number of cards in each set. Any missing or duplicate card triggers an alert or automatic ejection, ensuring each pack is accurate before final processing.
Stage 7: Packaging and Final Inspection
The final stage involves wrapping or boxing the assembled decks. This may include cellophane wrapping, tuck box folding, and barcode labeling. Quality control stations may perform visual inspections or weight checks to ensure consistency across all packaged products. The completed decks are then stacked and prepared for shipment.
Conclusion: Efficiency Through Integrated Workflow
A Playing Cards Making Machine delivers good production efficiency by combining these essential stages into a unified workflow. From feeding and printing to cutting and packaging, each step is designed to support high-volume, precision-driven output. Manufacturers benefit from reduced labor costs, faster production times, and consistent product quality, making automated card production a scalable and reliable solution for global demand.



 English
English عربى
عربى